You are Here: BLOG / CONCRETE REPAIR VS. REPLACEMENT: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE
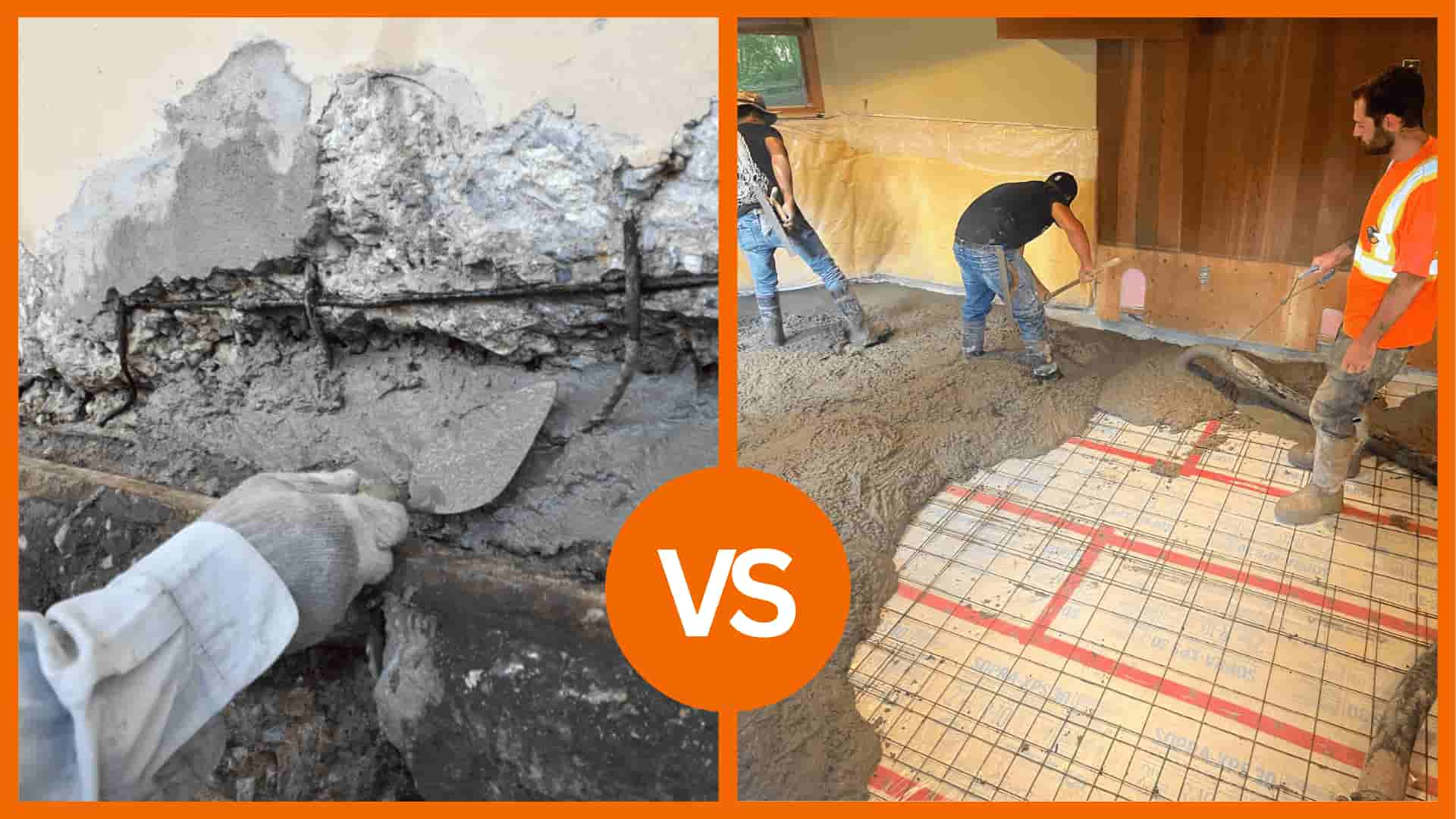

CONCRETE REPAIR VS REPLACEMENT: A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE
By TorontoConcreteRepair on August 19, 2024
Concrete is one of the most durable and widely used building materials, but it isn’t invincible. Over time, even the strongest concrete can develop cracks, surface damage, or structural issues. To make the right decision between concrete repair and replacement, a proper concrete assessment involving a visual inspection and structural survey is critical. This article will explore the differences between concrete repair and replacement, helping you determine which option best suits your needs.
Concrete Repair
Concrete repair involves fixing the damaged areas of concrete without replacing the entire structure. The methods used can vary depending on the extent and type of damage.
Methods
Concrete repair methods include crack injection, resurfacing, and patching. Crack injection involves filling small cracks with a specialized sealant, preventing water and other substances from entering and worsening the damage.
Resurfacing is used for large surface areas, where a new layer of concrete or a polymer-modified overlay is applied. Patching targets specific, localized damage by filling in missing or broken areas.
Common Scenarios for Concrete Repair
Concrete repair is often suitable for minor cracks, surface wear, and localized issues that don’t compromise the foundation stability. Driveways, sidewalks, and patios with superficial damage are prime candidates for repair.
Advantages of Concrete Repair
- Cost-Effective: Typically, repairs are less expensive than full replacement.
- Quick Solution: Most repairs can be done quickly with minimal disruption.
- Sustainable: Repairs reduce the waste generated by demolition and replacement while utilizing eco-friendly materials.
Concrete Replacement
Concrete replacement, as the name suggests, involves removing the existing damaged concrete and pouring new concrete in its place.
Methods
Concrete replacement includes full slab replacement, partial replacement, and sometimes a complete teardown and reconstruction. The method depends on the severity of the degradation, such as scaling, spalling, or significant erosion that affects the structure’s integrity.
Common Scenarios for Concrete Replacement
Concrete replacement is ideal when structural integrity is compromised, such as in cases of deep cracks, significant settling, or severe weather damage that affects the stability of the concrete.
Advantages of Concrete Replacement
- Long-Term Solution: Replacement offers a fresh start with new, stronger materials.
- Improved Aesthetics: The new concrete is smooth and free of patches or color mismatches.
- Enhanced Structural Integrity: Replacement ensures that no underlying issues like subgrade preparation or load-bearing problems are left unaddressed.
Differences between Concrete Repair & Replacement
Understanding the critical differences between repair and replacement can help guide your decision.
- Cost Comparison: Concrete repair is usually less expensive than replacement. However, multiple repairs over time can add up, making replacement more cost-effective in the long run.
- Time and Effort Involved: Repair projects are generally faster and less labor-intensive than replacement, which involves demolition, disposal, and pouring new concrete.
- Durability and Longevity: While repairs can extend the lifespan of existing concrete, replacement provides a brand-new surface, which is more durable and long-lasting, especially in terms of freeze-thaw resistance and flexural strength.
- Environmental Impact: Repair is more eco-friendly as it generates less waste. However, using sustainable construction materials during replacement can offset some environmental concerns.
When to Choose Concrete Repair?
Concrete repair is appropriate in several scenarios:
- Minor Cracks and Surface Damage: Small cracks and surface-level damage don’t usually require replacement. Repair techniques like crack injection and resurfacing can effectively address these issues.
- Early-Stage Deterioration: If the concrete shows signs of wear but is still structurally sound, repair can restore its appearance and function without the cost of replacement.
- Budget Constraints: If funds are limited, opting for repairs can buy you time before a more extensive replacement is necessary.
When to Choose Concrete Replacement?
There are times when replacement is the better choice:
- Severe Structural Damage: When the foundation or support is compromised, replacement is essential to prevent further deterioration and ensure safety.
- Old and Worn-Out Concrete: If the concrete is nearing the end of its lifespan or has been repaired multiple times, replacement might be more practical.
- Long-Term Investment Perspective: For property owners looking to increase value or avoid recurring repair costs, replacement offers a more permanent solution.
Concrete Repair Techniques
Several methods are commonly used in concrete repair:
- Crack Injection: Crack injection involves injecting a polyurethane or epoxy sealant into the crack to bond the concrete back together and seal it from moisture.
- Resurfacing: Resurfacing covers larger areas with a new concrete layer, improving appearance and function.
- Patching: Patching involves filling in small holes or chips with a concrete mix or a pre-made patching compound.
Concrete Replacement Techniques
Concrete replacement can involve different approaches depending on the extent of the damage:
- Full Slab Replacement:This involves removing the entire slab and pouring a new one in its place.
- Partial Replacement: Only sections of the concrete are replaced, leaving undamaged areas intact.
- Demolition and Reconstruction: For heavily damaged structures, demolishing and rebuilding from scratch may be the best option.
Cost Analysis
Cost plays a significant role in the decision-making process.
- Initial Costs: Repair is generally less expensive upfront. However, recurring repairs can add up over time.
- Long-Term Costs: Replacement might be more costly initially but can save money in the long term by reducing the need for future repairs.
- Hidden Costs: Replacement projects might involve additional expenses like excavation, disposal, and landscaping restoration.
Time Considerations
Time is another essential factor:
- Time to Complete the Project: Repair jobs are quicker, often completed within a day. Replacement projects take longer due to the need for demolition, setting, and curing time.
- Downtime and Disruption: Repair involves minimal disruption, while replacement might require you to avoid the area for several days.
Environmental and Sustainability Factors
Environmental concerns are increasingly important in construction decisions:
- Repair: Reducing Waste
Repairing rather than replacing helps reduce the amount of concrete waste sent to landfills.
- Replacement: Using Sustainable Materials
Modern concrete replacements can use eco-friendly materials and techniques, mitigating the environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Contractor
The success of either repair or replacement largely depends on the contractor’s expertise.
- What to Look for in a Concrete Specialist: Look for experience, references, and knowledge of both repair and replacement techniques.
- Questions to Ask Before Hiring: Ask about their experience with similar projects, warranties offered, and the expected timeline.
- Common Mistakes to Avoid: Some pitfalls can derail your concrete project:
- Misjudging the Severity of Damage: A professional assessment is crucial; what looks like a small crack could indicate deeper issues.
- Skipping Professional Inspection: Always get a professional opinion before deciding between repair and replacement.
- Focusing Only on Short-Term Costs: Consider the long-term implications of your decision, including maintenance and lifespan.
FAQs
How Long Does a Repair Last?
Well-done repairs can last 5-10 years, depending on factors like traffic, weather, and material quality.
How Long Does a Replacement Last?
Newly poured concrete can last 25-30 years or more if properly maintained.
Is it cheaper to repair or replace concrete?
Repair is usually cheaper upfront, but replacement can be more cost-effective in the long run if recurring repairs are needed.
How do I know if my concrete needs to be replaced?
Severe structural damage, deep cracks, and settling are indicators that replacement may be necessary.
Can concrete repair be a DIY project?
Minor repairs like crack filling can be DIY, but more extensive repairs require professional expertise.
How long does a concrete repair last?
A well-done repair can last 5-10 years, depending on conditions.
Does replacing concrete increase property value?
Yes, replacing damaged concrete with new, well-finished concrete can improve curb appeal and increase property value.
Conclusion
When deciding between concrete repair and replacement, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. Minor damage often warrants repair, offering a quick and cost-effective solution.
However, when foundation stability is compromised or long-term durability is a priority, replacement is the better option. By weighing the pros and cons, assessing the damage, and consulting with a professional, you can make the best decision for your property.
Still if you have any confusion, or want to ask questions more about concrete repair or concrete replacement, you can contact us, we are happy to assist you anyhow. You can reach out to us over a phone call or from email or from our social media page.